How does the cosmic web impact galaxy formation?


Corentin Cadiou — PhD student
In collaboration with Yohan Dubois, Christophe Pichon, Marcello Musso
MPA — 18/12/2018

An insight from theory and numerical simulations.
(Quick) Introduction
A very biased view on galaxy formation
The isotropic view

Silk&Mamon 12
Press&Schechter 74
"Mass function from first principle"
Works nicely to describe anisotropic features in the Universe
Marginalise position
The anisotropic view
Galaxies do not form anywhere at anytime
Need to create anisotropic methods → beyond two-point correlation function
Structure in the GAMA survey, Kraljic+18
How to measure position?
What metric modulates galaxy properties?
Predicting anisotropic halo properties
Excursion Set Theory
Galaxy properties & evolution from initial conditions
⇒ Find largest mass that will collapse by z at given location
| Theory | Real space |
|---|---|
| R | M |
| z |
Spherical collapse model:
Structure of size R will collapse at z iff
R
Compressing the spatial information

Height: determined by (over-)density
Curvature: controlled by (traceless) tidal tensor
Poisson equation
Critical point constrain*
* we work in the free-falling frame
Results



Direction of void
Direction of filament
In filaments, halos are...
- more massive
- form later (at fixed mass)
- accrete more (at fixed mass)
... than in voids
(Musso, Cadiou et al 2018)
Excursion set theory + saddle point constrain


Results


The results hold for galaxies (at least simulated ones)!
Some open questions / improvements
- Develop more subtle quantities
- concentration, spin quantities, etc...
- two-filament configuration (bridge effect)
- merger rate (extending Hanami 01)
- beyond spherical collapse? Ask Marcello Musso!
- Take into account tidal effects…
- by improving ES with moving barrier (e.g. Castorina+16)
- using peak patch theory
- Effective models of galaxy formation? (Kraljic+18)
Galaxies seem to be influenced by the cosmic web too...

This is largely WIP
Can we explain this?
We can try using numerical simulations
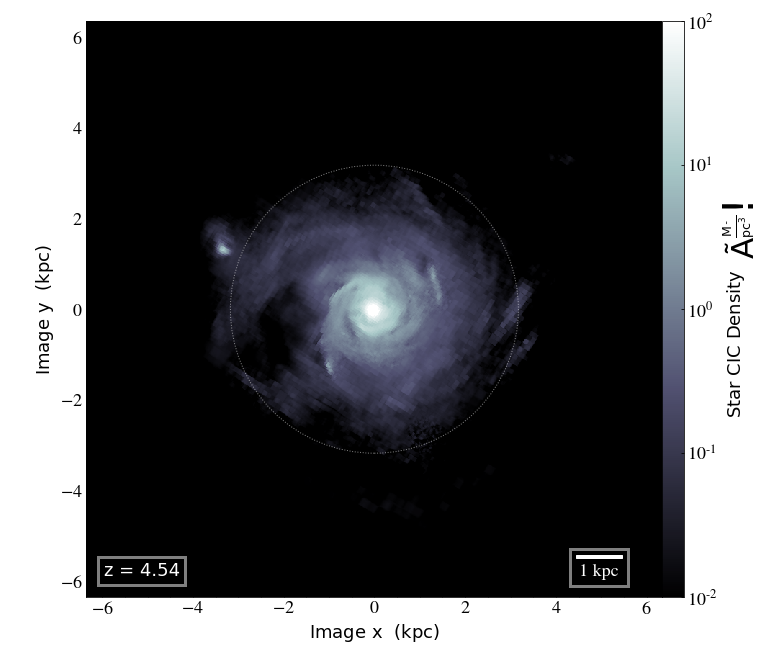
Simulation Setup
- suite of zoom-in simulations (~3-5), RAMSES (Teyssier 2002)
- Δx = 35pc, Mstar = 1.1 10⁴ M☉ Mhalo=10¹² M☉
- Turbulent star formation (Kimm+17, Trebitsch+17)
- Mechanical feedback (Kimm+15)
- AGN formation with spin-regulated efficiency (Dubois+12,+14)
- 30,000,000 tracer particles (~10/cell, 0.5/star, Cadiou+18)

*See Cadiou+18
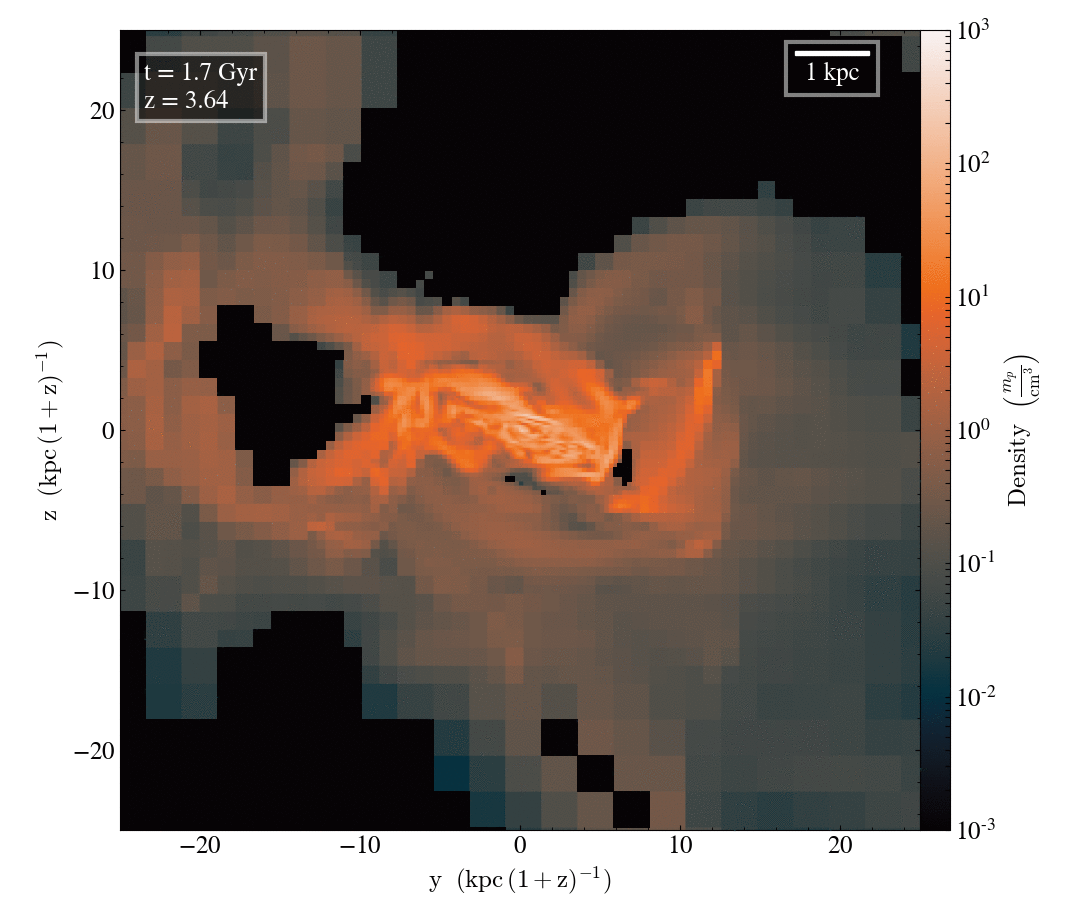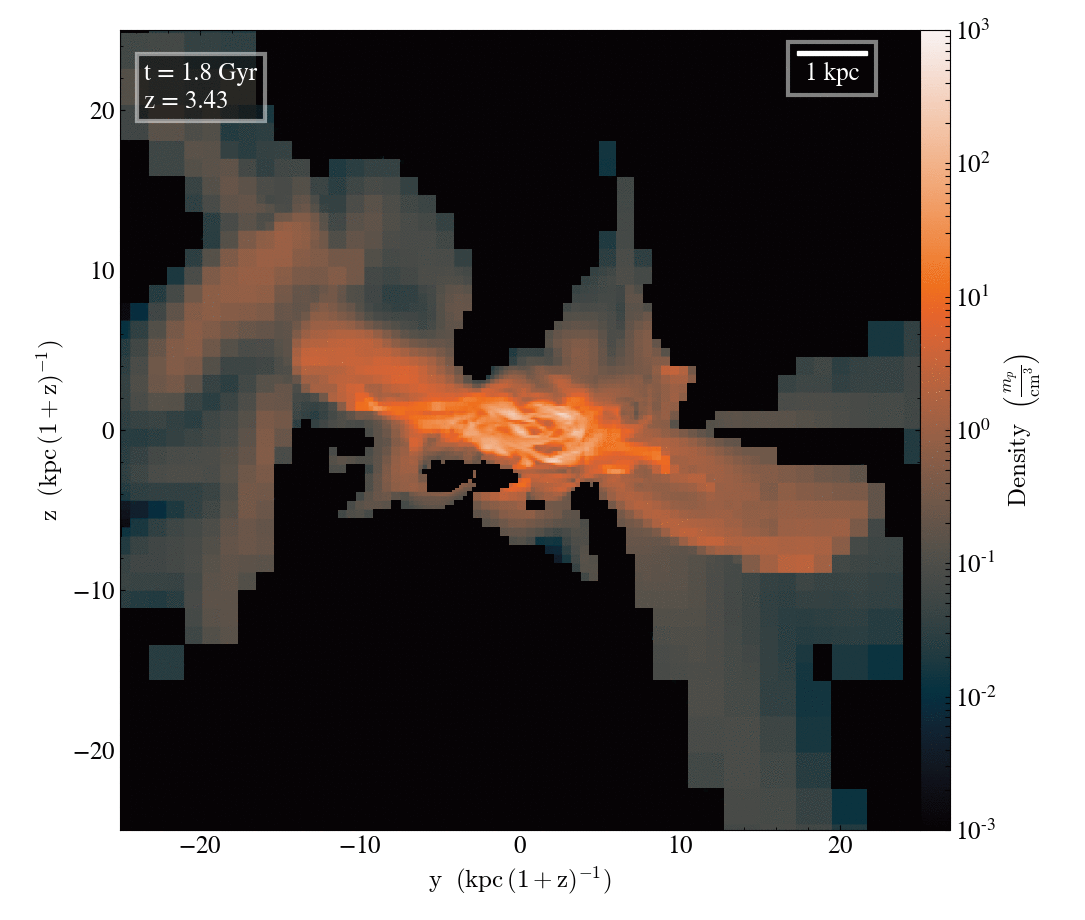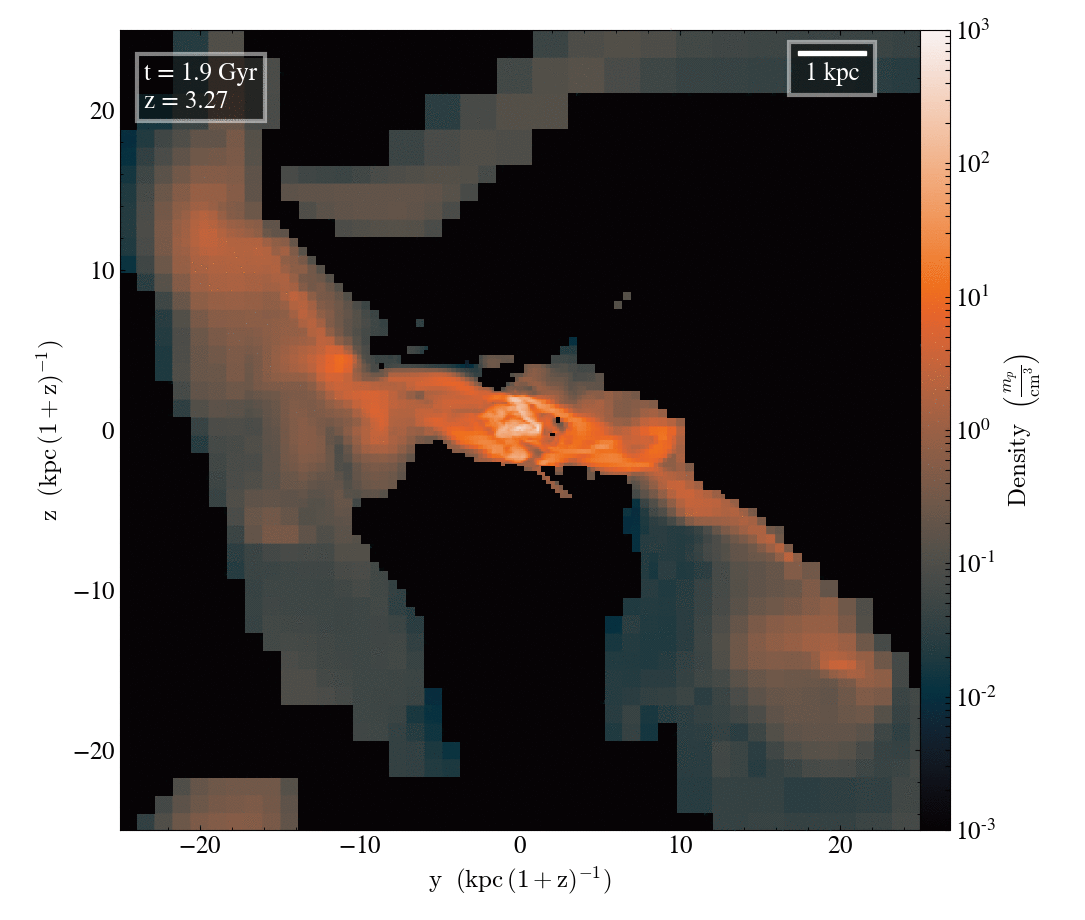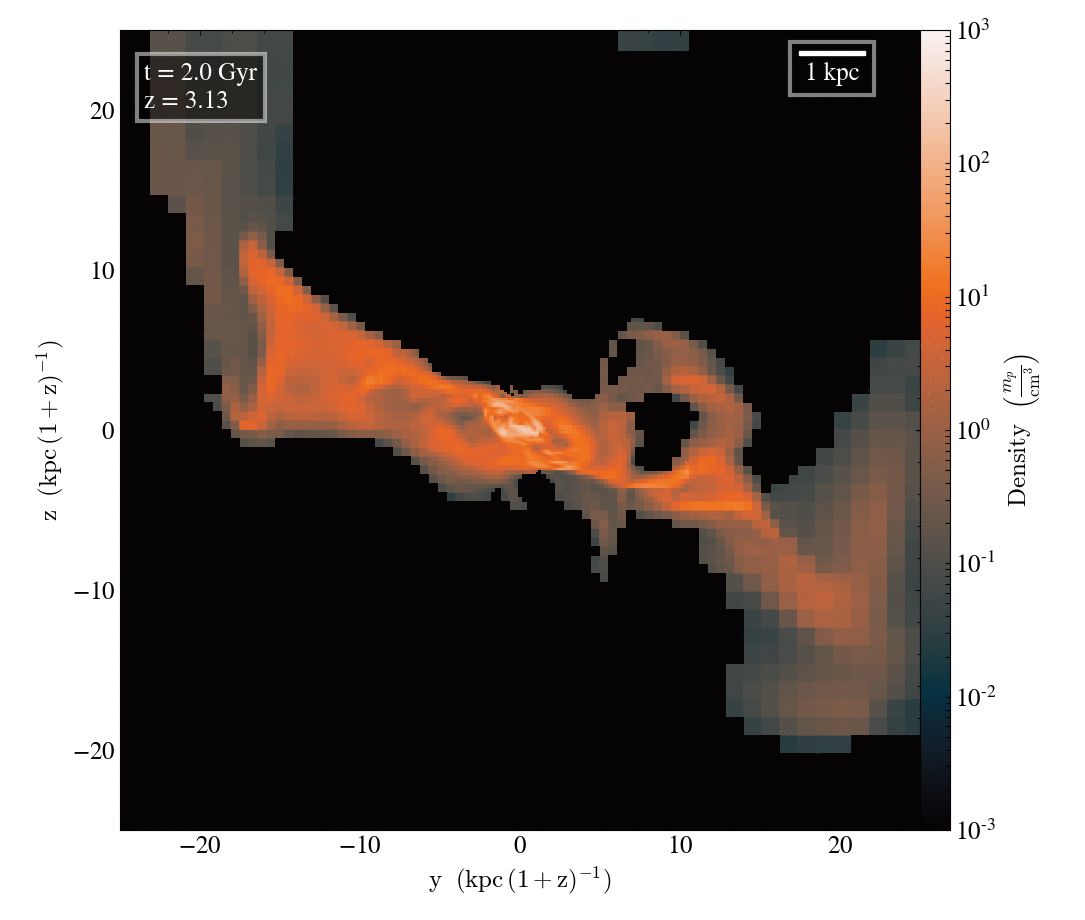
Gas density
Tracer density
Linking assembly variables to
galaxy formation?
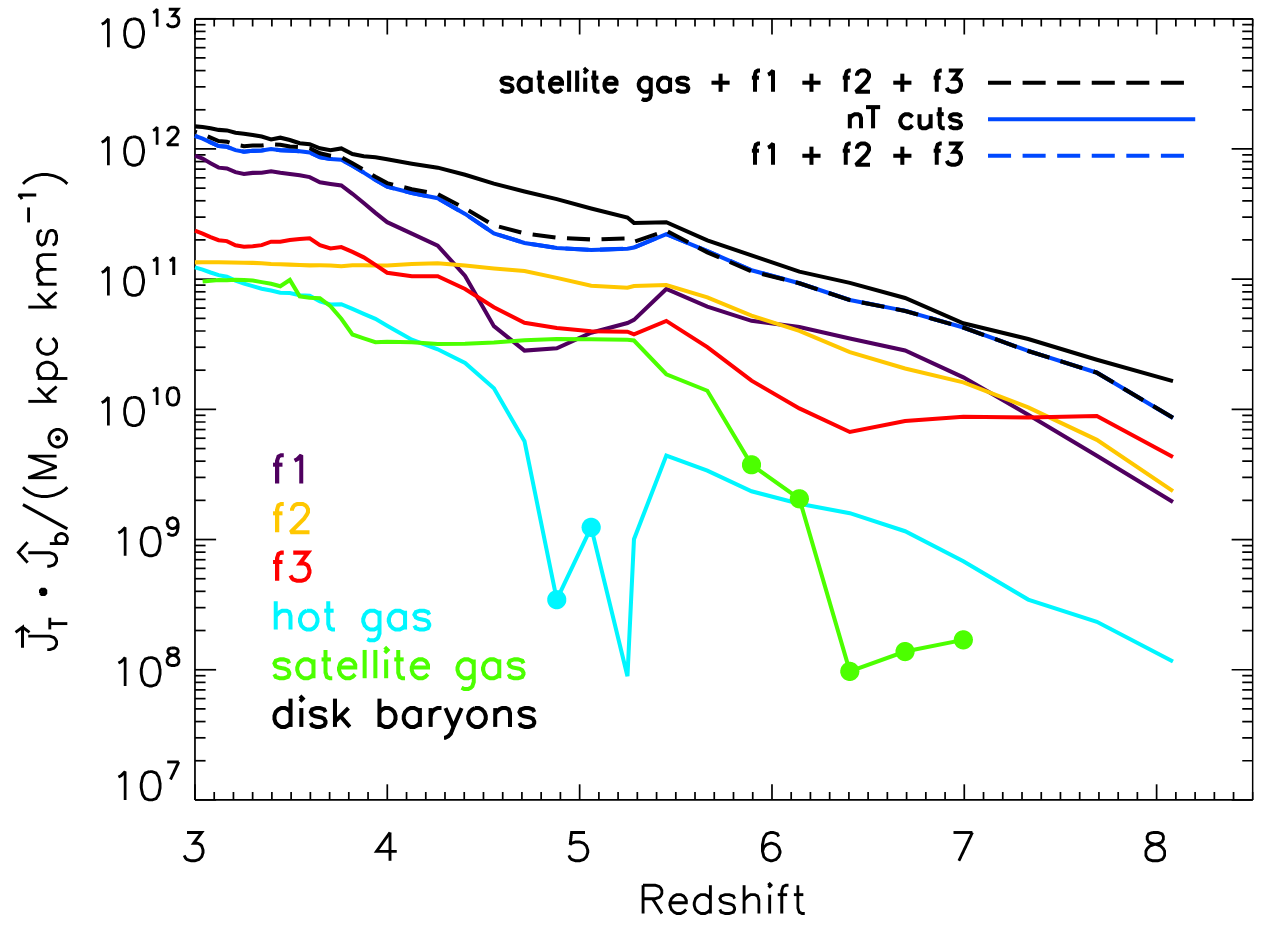
Filamentary accretion is responsible for most of the mass and angular momentum acquisition (at z>3 ; Kereš+05, Pichon+11, Tillson+12, …)
Filamentary accretion: natural "bridge" between large scale structures (cosmic web) and galaxy formation

Tillson+2015
Cadiou+ in prep
Linking assembly variables to
galaxy formation?

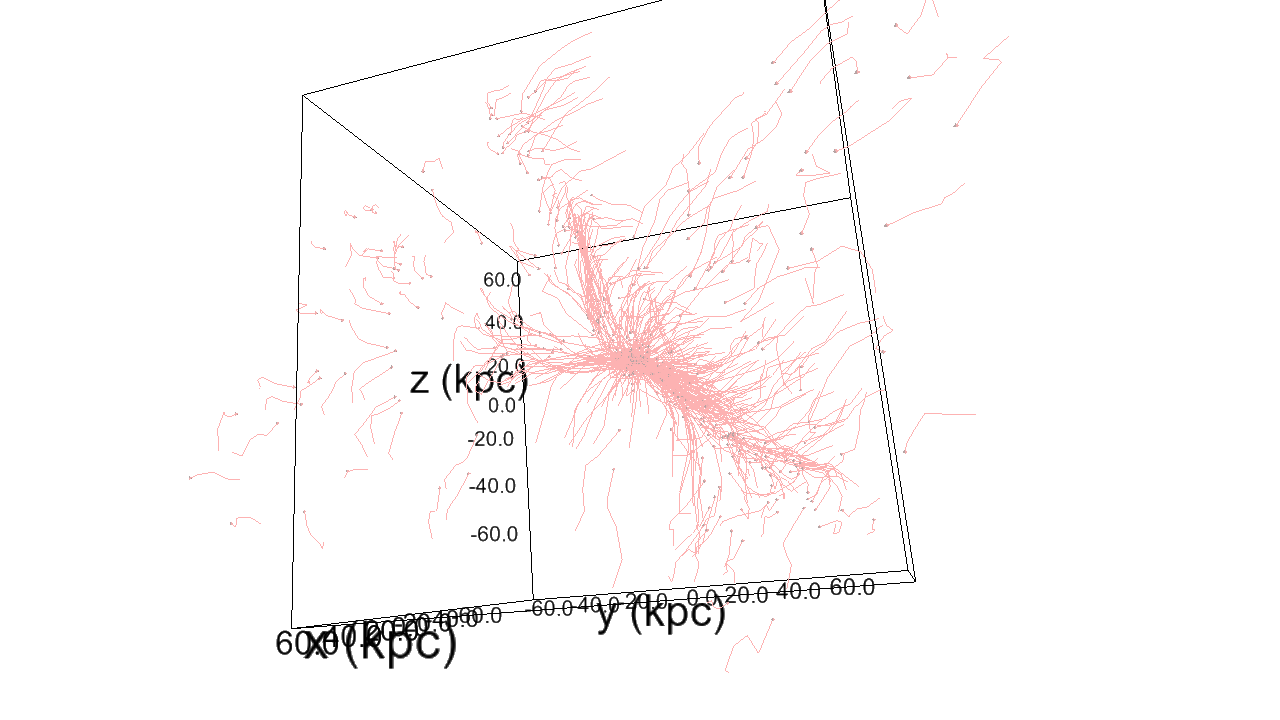
The structure of filamentary accretion
The cold flows are
- coherent
- resilient
- source at large scales
- end up at small scales
- sAM rich
for small enough galaxies/high z
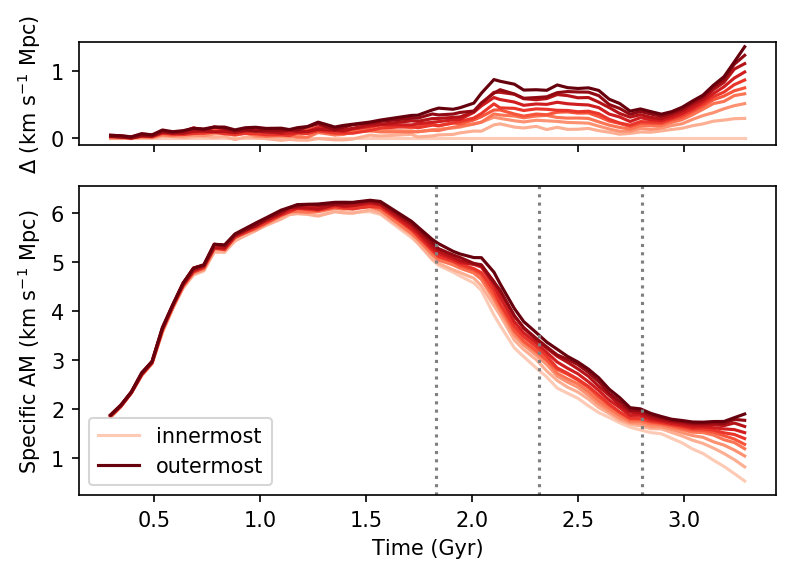
Time →
High sAM →
Innermost regions
Outermost regions
Cadiou+ in prep
Perfect candidates to transport anisotropic information from cosmic web to smale scales.
Tillson+15
Cold accretion and angular momentum
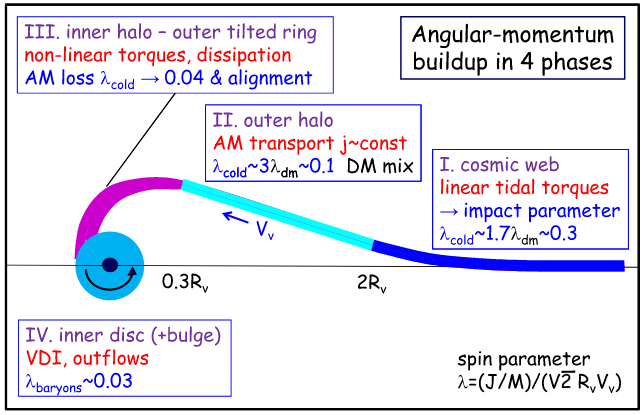

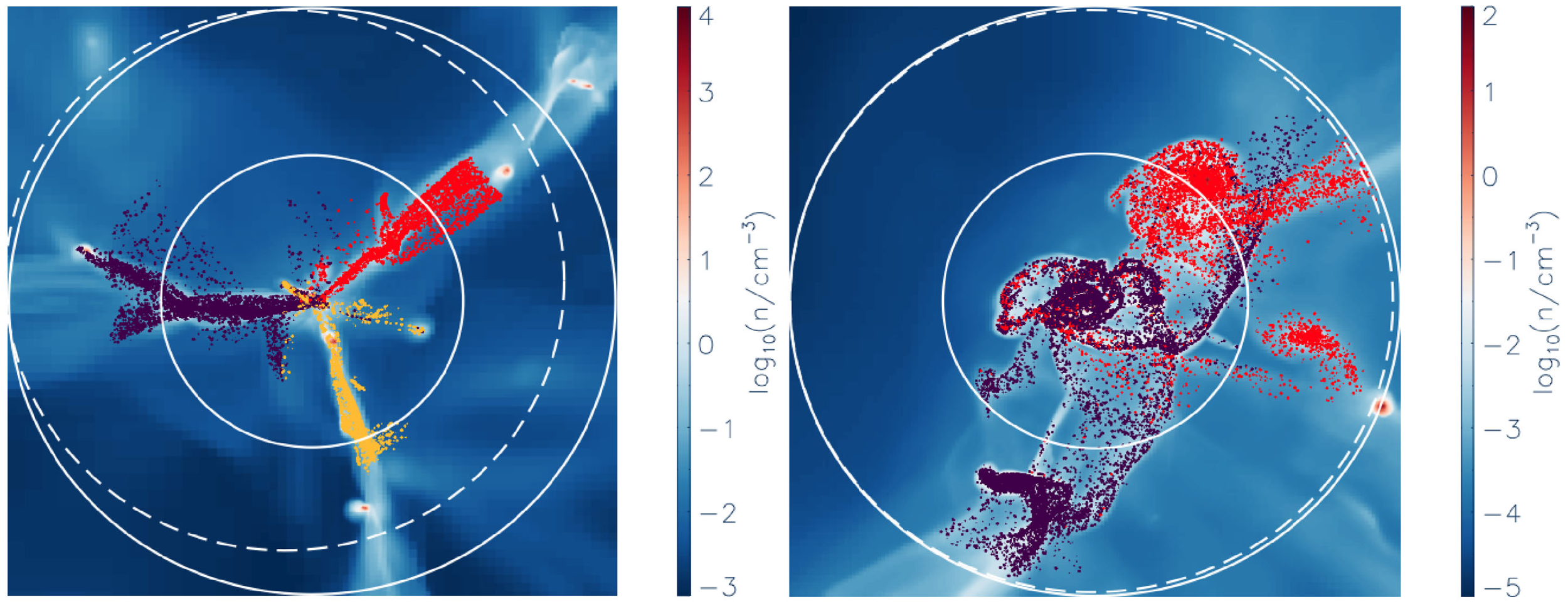
Danovich+15
- AM acquisition via TTT >2Rvir
- AM transport down to >0.3Rvir
- AM loss in inner halo >0.1Rvir
- AM loss in inner disk <0.1Rvir
1
2
3
4

Cadiou+ in prep
- Cause of AM dissipation in internal halo?
- Gravitational torques? (Danovich+15)
- Hydrodynamical shock? (Cadiou & Ramsoy, Devriendt+ in prep)
- AGN/SN feedback? (Nelson+15)
- KH instability? (Mandelker+18)
- sAM content of gas just prior to star formation?
- Alignment of cold flows with large-scale filaments?
- sAM due to filament "sweep" or impact parameter?
- Effect of three-filament configuration (Cadiou&Pichon, in prep)
Some open questions / improvements
Thank you
New Horizon simulation, Dubois+ in prep
PS: I am available for a postdoc!
Backup Slides
Galaxy properties
Bulge
Red or blue?
Disk
All the properties vary with cosmic time…
Do they vary with spatial location?
Galaxies & the cosmic web
Halo model: galaxy properties are inherited from their parent halo + local density (~no effect of the cosmic web)
-
Kaiser bias: large scale overdensities bias halo density
(Kaiser 84, BBKS 86)
- Spins align with the cosmic web
(Tempel&Libeskind 13, Codis+15, Chisari+15, ...)
-
Galaxy properties are modulated by the cosmic web
(Laigle+17, Kraljic+18, Musso, Cadiou+18)


We have to take into account the spatial modulation induced by the cosmic web
How do galactic and DM halo scales couple to the large scale anisotropies of the cosmic web?
The Excursion Set Theory
Excursion Set Theory
Galaxy properties & evolution from initial conditions
⇒ Find largest mass that will collapse by z at given location
Large mass Small mass
Early collapse
Late collapse
Constrained Excursion Set Theory
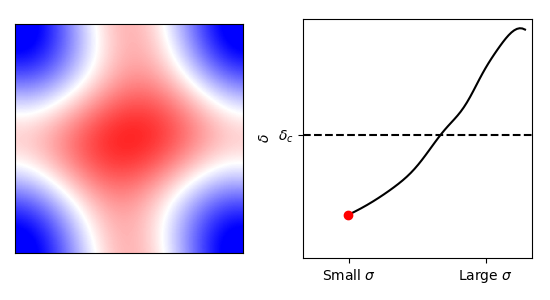
+

``How does the cosmic web biases the excursion and halo properties?´´
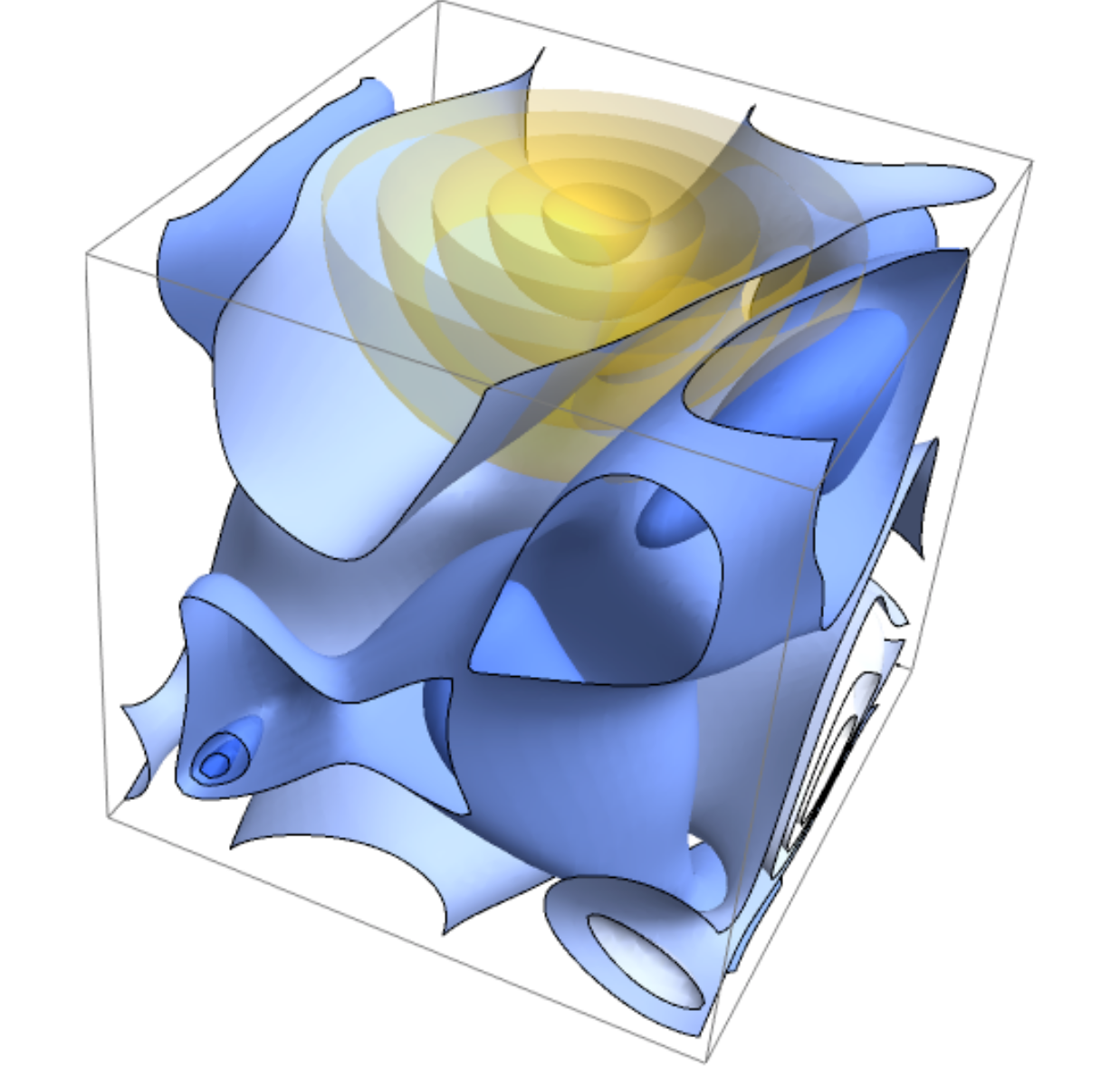
The Cosmic Web
How to encode the cosmic web?
Nodes (maxima of density)
Saddle point (center of filament)

Compressing the spatial information
1
2
3
Describe the critical points only
Results
Results
The relevant parameter for quantifying the anisotropy is:


Observation (in simu)
v/σ residuals at fixed dens + mass
Theory

But... why?

The filament constrains
- the density
- the variance of the density

Void Filament Void

Conclusion
Conclusions...
- New model built, room for lots of improvement
- Classical results recovered
- Help to uncover new results
...and perspectives
Towards a more comprehensive halo model
- How do galaxy respond to large-scale anisotropies?
⇒ simulations (WIP) - Take into account non spherical collapse (WIP)
- More subtle quantities:
- halo merger rate (WIP)
- halo concentration
- ... star formation rate?

Excursion set at fixed final mass in different environments

Excursion set at fixed final mass in different environments

Effect of AGN feedback
Simulation Setup
How did the disk acquire its AM?
Requires the knowledge of the Lagrangian evolution of the gas
⇒ now possible using tracer particles
Let look at the filamentary accretion of cold gas at z≥2